
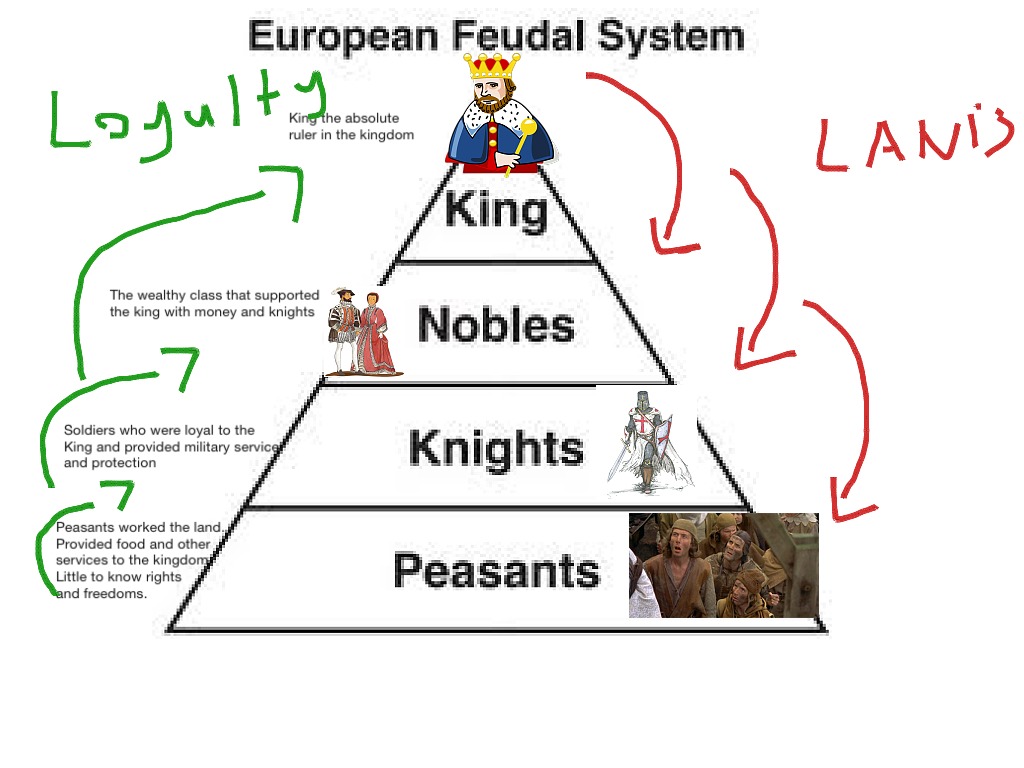
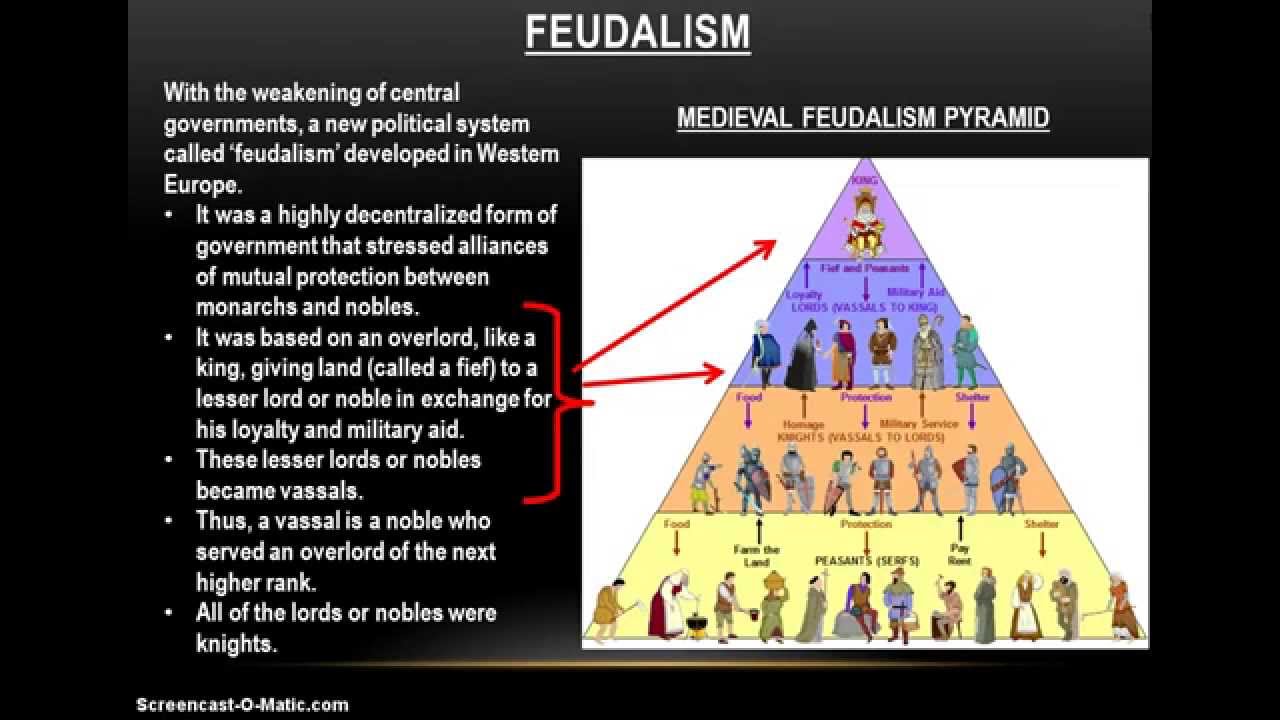
Thus, a landed aristocracy dominated the government in the feudal system.In theory, the king could reclaim a disloyal vassal's fief, but in practise, this was rarely done. The chiefs, in turn, could appoint sub-chiefs as vassals and allot them a portion of their fief.The king used one method to control this: he swore the chiefs to an oath of loyalty to him as his vassals and, in exchange, recognised the tract of land dominated by the chiefs as their fiefs.The monarchy grew stronger over time, and an attempt was made to limit the power of the chiefs, who constantly fought each other, resulting in a state of social anarchy. The king was no different than one of the more powerful feudal chiefs.The most powerful elements in this society were the chiefs, who dominated large tracts of land and also played an important role in government with their military following.
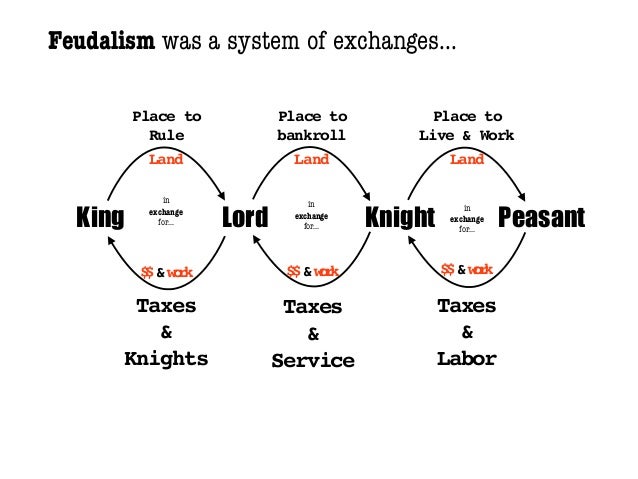
This is derived from the Latin word feudum, which became fief in English.Feudalism is the name given to the new order that gradually emerged. Following the disintegration of the Roman empire, a new type of society and a new system of government arose in Western Europe.Universities played an important role in the spread of new knowledge and ideas, which eventually led to the Renaissance and the rise of a new Europe.The period was notable for the advancement of science and technology, the expansion of towns, and the establishment of universities in a number of cities, including Padua and Milan in Italy.Western Europe was able to regain a high level of prosperity between the twelfth and fourteenth centuries.However, this was also a period of agricultural expansion, which paved the way for the revival of city life in the tenth century, as well as the expansion of foreign trade.Historians have long referred to the period between the sixth and tenth centuries as the "Dark Age." One reason for this was the lack of gold, which the Romans had obtained from Africa and used in their trade with the Orient.For centuries after the fall of the Roman Empire in the West, cities virtually vanished in Western Europe.It finally vanished in the middle of the fifteenth century, when Constantinople was conquered by the Turks.It also served as a link between the Greco-Roman civilization and the Arab world, and it later contributed to the revival of Greek learning in the West.It established government and cultural traditions, many of which were later absorbed by the Arabs after they conquered Syria and Egypt.The Byzantine empire was a large and flourishing empire that continued to trade with Asia after the Roman empire in the West collapsed.
Russia was converted to Christianity as a result of its efforts and those of the Byzantine rulers. The Greek Orthodox Church was the name given to the church in the East. However, it differed greatly from the Catholic Church in the West, which had its headquarters in Rome, in terms of belief and ritual.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
